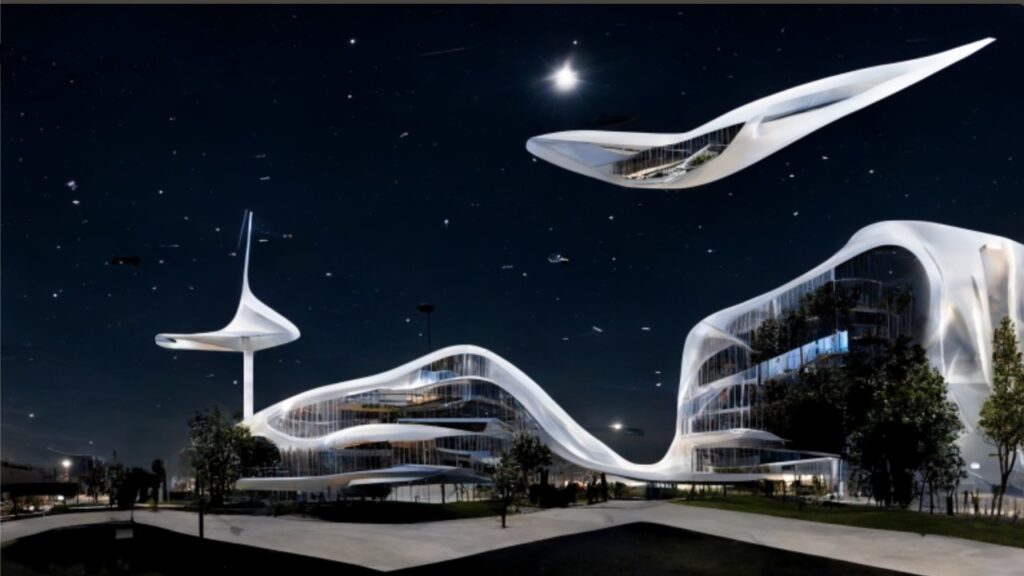
HOSPITAL OF THE FUTURE
Our “Hospital of the Future” vision is a paradigm shift that will help drive systemic change in response to pressing health, social and environmental issues. We combine architecture and engineering, medical planning, sustainable design, evidence-based design, and systems thinking approaches to respond to the complex challenges of today, innovatively, and effectively, by building a smart and resilient future for all our tomorrows.
We are working to develop a visionary approach that remodels and redefines healthcare delivery by peeling away the areas within the clinical setting that need not be in a costly, physically built space, and developing a reduced footprint solution that becomes a “hospital without walls”.
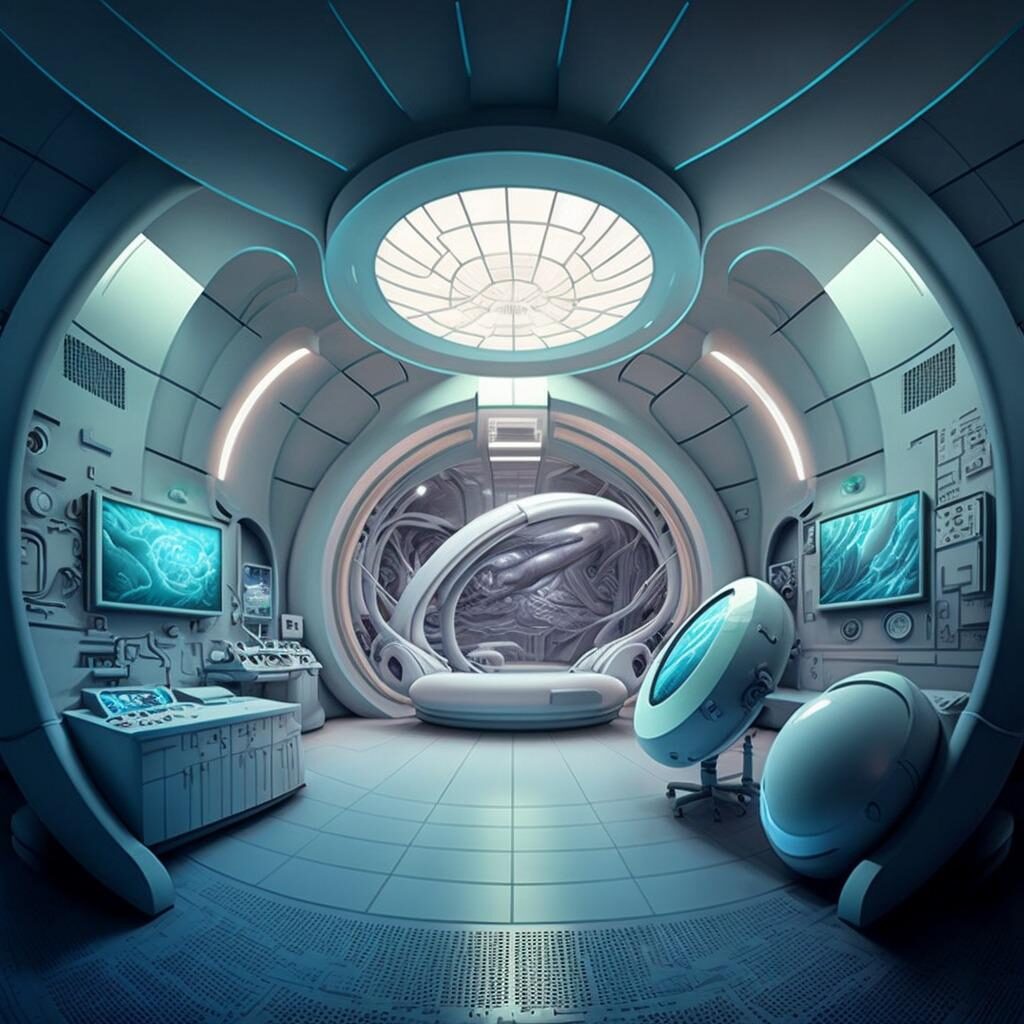
In support of an ongoing healthcare innovation that is embracing MedTech and acquiring a new digital identity we bring the next generation of telemedicine that centralises digital cloud technologies, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), and using technology as an exponent of sustainability, the spaces for our hospital without walls’ clinical consultations are proposed to primarily be located in the Metaverse, along with virtual learning, clinical simulation, and development.
No longer limited to the “playground” methodology that was first envisaged, patients will be able to meet remotely with their clinical teams, clinicians can collaborate, meet, and train with each other within AI designed spaces developed by our newly formed tangramMETA team. Our innovation and advanced technology group, created to harness the potential of digital and virtual technologies as a supporter of environmentally conscious, sustainable designs.
Nor, incorporating the costs of structure, of building fabric, of materials specified for infection control, or of advanced building and medical services installations. Calming interior designs and sound waves can be produced to support the therapeutic, healing environment that is within a virtual location, one which does not impose on any other patient or staff activity within any costly clinical setting.
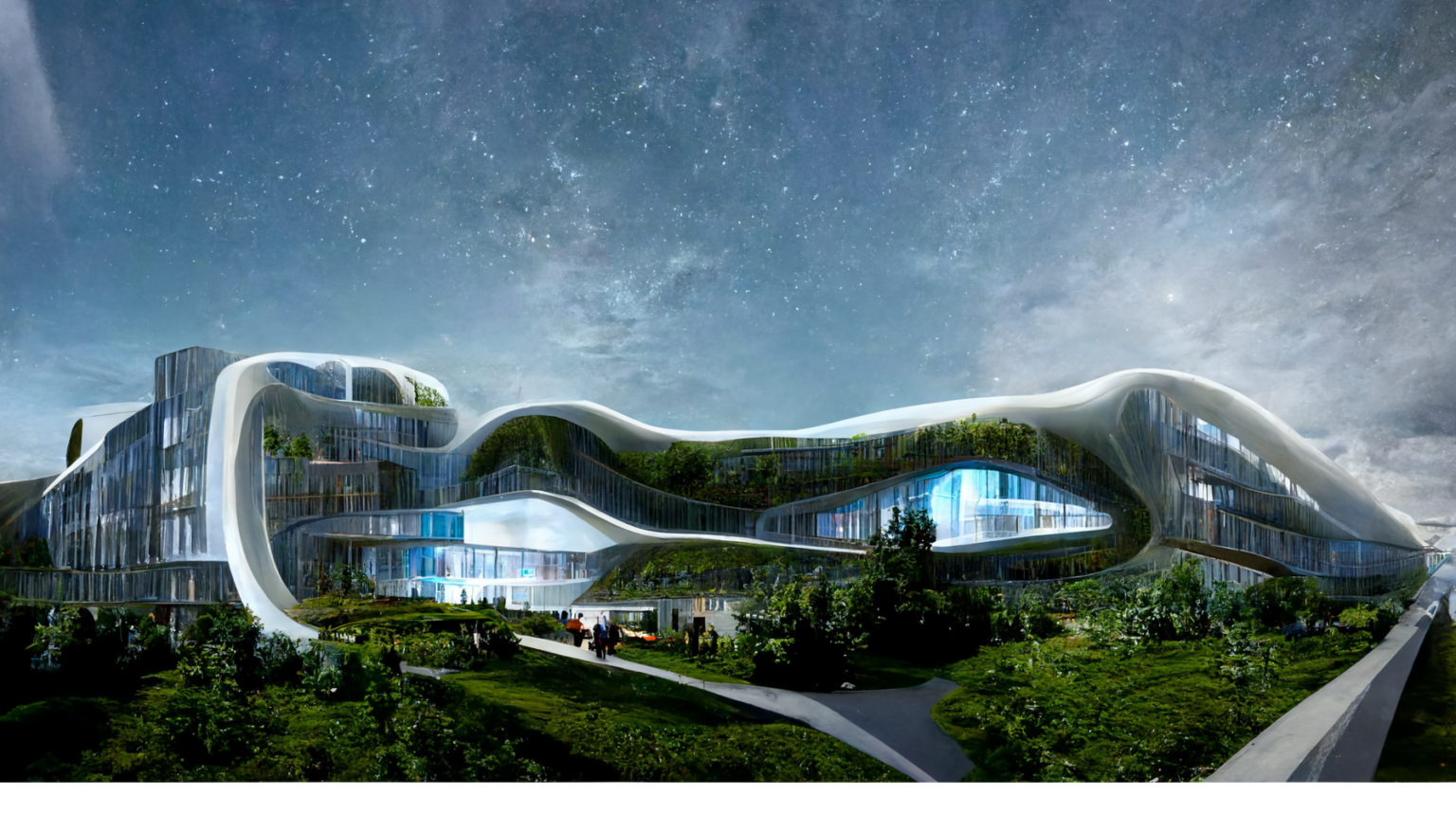



Our Green Strategy
Creating the Hospital of the Future that optimises eco-designs and sustainable solutions that
are designed in accordance with the World Health Organisation’s 7 elements of a climate friendly hospital, which addresses and responds in support of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and targets, we are working to achieve a radical reduction in carbon, water, and waste footprints, along with capital and operational costs.
In working to ensure a more sustainable future, this is the sector which must be a focus area as we move forwards. Be it climate, chemicals in the environment, the healthcare industry is such a large part of the problem. Delivering better solutions here will be key to resolving many of our global challenges. Thus, our next generation of healthcare facilities must be more resilient, better designed and built to protect the environment. Hospitals must become better connected to smarter, digitised, intelligent ecosystems within the city, the community and home, to respond more responsibly, as we shape a very different future.
Currently hospital buildings as a typology are notoriously high on the continual usage of energy and water whilst releasing 2.5 times the Greenhouse House Gas (GHG) emissions of most similar sized commercial buildings, 6% of which is made up of nitrous oxide, a toxic gas 300 times more destructive to the environment than carbon dioxide, along with hazardous waste, for the safe disposal of which more than half the countries in the world leave unregulated. These facts condemn the global healthcare sector to being the second worst “environmentally” performing industry globally.
The shift to constructing sustainable healthcare facilities is largely cantered on reducing the carbon burden in hospitals whilst ensuring that the occupants are kept safe, and environmental impact is minimised.
Therefore, it remains essential to involve the incorporation of green designs and concepts into the process to reduce the impact on the environment, cut down operational costs, and increase energy efficiency to allow owners and operators to reduce their carbon footprint.
There is no global standard that defines what a ‘green and healthy hospital’ is or should be, at tangram we are into our 4th decade of delivering healthcare projects in the region that respond individually to their own specific location and climate. We always advocate the incorporation of passive sustainable designs in the siting, construction and landscaping of our projects and incorporate biophilic elements to bring in the calming natural world for its’ healing and therapeutic properties as we work toward zero – zero carbon, zero waste, zero emissions.
Bringing a new green strategy to the physical building stock, by introducing a range of Modern Methods of Construction (MMC) delivery options in a factory to frame approach. And, in our commitment to collaborative project working, we are embracing digital technology from the outset of each project to allow us to move seamlessly from conception through to delivery, reducing risk and optimising value and programme along with minimising the impacts that the building has on the environment.

Modern Methods of Construction (MMC)
Offsite technologies and smart digital construction techniques are now recognised as being integral to providing critical solutions to many of the complex challenges facing the construction industry today as we must drive change and reform the way in which we build to enable the much-needed transformation to a decarbonised future.
Panelised, volumetric modular systems, pod and prefabricated MEP solutions are growing in popularity, thus, adopting a MMC approach and moving more of the build into a factory setting can significantly reduce the carbon emissions of a building or structure.

Embodied Carbon
This is the carbon emissions associated with the materials and construction process es throughout the entire lifecycle of a building or structure.
Manufacturing processes produce much less carbon than traditional onsite construction processes.
There can be much less transportation needed to be used reducing the constant flow of trucks and lorries in and out of site with materials or products and components to be put together from different points of origin. Once factory prefabrication is complete it can be delivered to site quickly in a programmed and efficient single series of agreed deliveries, saving upto 40% of transportation needs, reducing time, cost and pollution.
Waste also can be drastically reduced, the standardised size and fixings of components and repetitive processes creates much more accuracy in production and gives less room for errors, enabling better control of material quantities needed to be available. By allowing for a more strategic workflow which can be more precisely monitored, honed, and managed, material wastage can be minimised. This will reduce waste generation which combined with improving recycling, reuse, and circularity of most typically perceived “waste products” which can then be diverted from landfill.

Operational Net-Zero Carbon
This is when the net amount of carbon emissions associated with the building’s operational energy, on an annual basis, is equal to or less than zero. Operational energy consists of the annual amount of energy required for heating, cooling, lighting, and power.
This part of the net-zero element is influenced in the design stages of construction. MMC and offsite construction can offer a controlled manufacturing process that is able to deliver to a higher quality and to more of a certainty of achieving the required performance levels for low U values, good insulation, and minimal air leakage etc. This manufacturing process also produces greater levels of air tightness and an overall improved building performance. All instrumental in ensuring buildings meet operational net-zero requirements.
Advancing to net-zero carbon can prove to be key for the delivery of any future hospital and any buildings of growing complexities, hospitals are the very microcosms of our cities, we must not shirk from our responsibilities as designers and must prepare these costly, physical assets for adaptability, disassembly, and reuse.
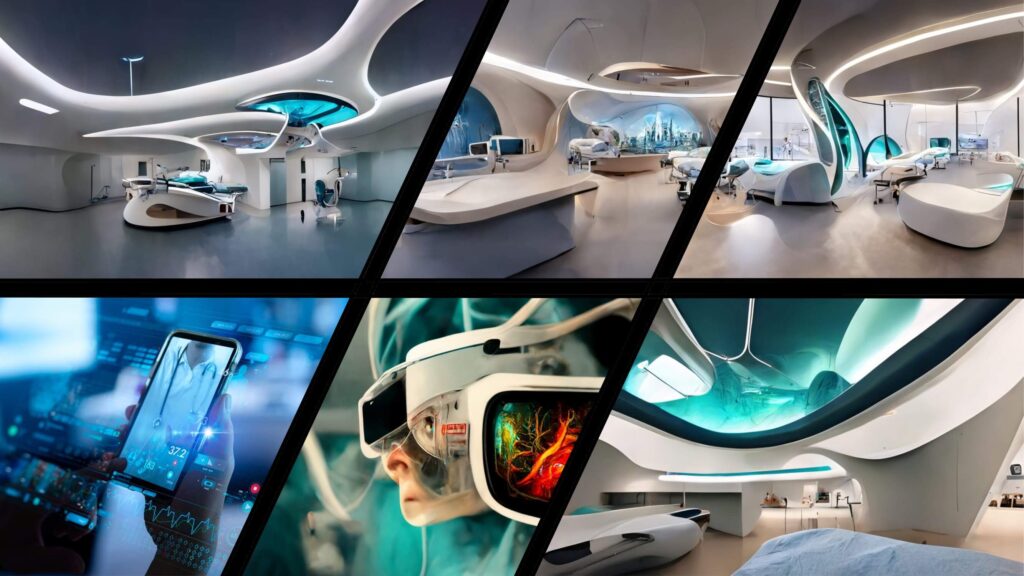
The Healing Environment
Critical to all our work in the healthcare sector, is creating a healing environment that has nurturing and therapeutic effects is key. Research shows that well designed healthcare environments can reduce patients stress and anxiety, accelerate recovery, reduce lengths of inpatient stays and medication use, along with promoting an improved sense of well-being, improving patient outcomes. Additionally, staff and visitor experiences are improved, satisfaction and productivity rates increase and positivity’s in staff recruitment and retention are achieved.
We ensure that natural light, calming interior design, improved internal air quality and comfort levels that include noise reduction are all combined with the psychology of colour, textures and the inclusion of the building at one with nature, both internally and externally. Making hospitals healthier places to stay, visit and work in.

Virtual Hospital and Cyber Clinics
To provide a patient-centric remote care model that reduces patient visits to hospitals and by delivering healthcare to where patients live, and work will break down the walls and remove the need for many outpatient consultations and functions to be held within costly, centralised facilities that can concentrate on the care of our more needy patients as we expand on the now familiar telemedicine platforms which have grown in usage over the last few years.
Utilising affordable remote diagnostics and monitoring via sensors, apps, and equipment connecting patient and clinical team through web-based or smartphone apps, advances in technology can make it easier for more people to access healthcare, in convenient locations when and how they need to. Telehealth is especially helpful to monitor and improve ongoing health issues, such as medication changes or chronic health conditions. enabling quick and easy data flow between clinicians and patients, utilising existing continuous home clinical monitoring techniques to relay data, home sample collection methods for ease of delivery for lab analysis and courier deliveries for prescriptions. Reducing the need for patient and medication management to take place in costly clinical settings.
For remote communities and patients unable to access or use web-based equipment, physical cyber clinics will be created, where trained staff can aid those who need it to use equipment provided to access this service with privacy. Such facilities will take the cost pressures off as they are removed from the costly clinical staffing and servicing of more acute level spaces.
Consultations with clinicians who also may be sitting outside of costly acute settings, and will be relayed electronically, and held within virtual spaces, designed using AI and based in the Metaverse. Where the cost of creating calming, relaxing and therapeutic healing environments are free of the more expensive physical constraints, of structure, building fabric, infection control management, servicing, and cleaning.
We utilise blockchain technologies to structure, code and store all sensitive health data with inherent security that simplifies health information exchanges.
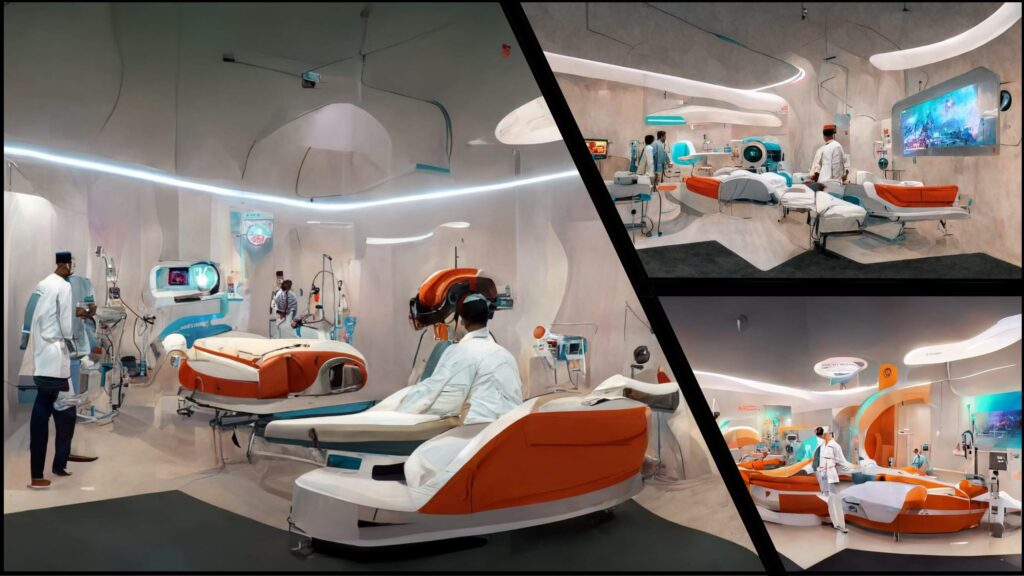
Virtual learning and development
Virtual training will become more prevalent in the future, though, never fully replacing hands-on, in-person medical training and simulation. The opportunities to carry out much of this remotely and collaboratively in spaces created in the Metaverse will bring wider and more diverse participation. It will alleviate time and cost constraints, whilst being more accessible to all.
Our Hospital of the Future typology is based on patient-centric care which reduces the cost of healthcare delivery, whilst improving its efficiency, access, and quality. It may look very different from the hospital of today as it responds to the speed, capacity and quality of growth needed across the sector, and physically offers only services that cannot be digitised. We must all take steps to reduce the carbon burden on the environment, reducing and transforming how we build is critical to not only our own health, but to the health of our planet.
